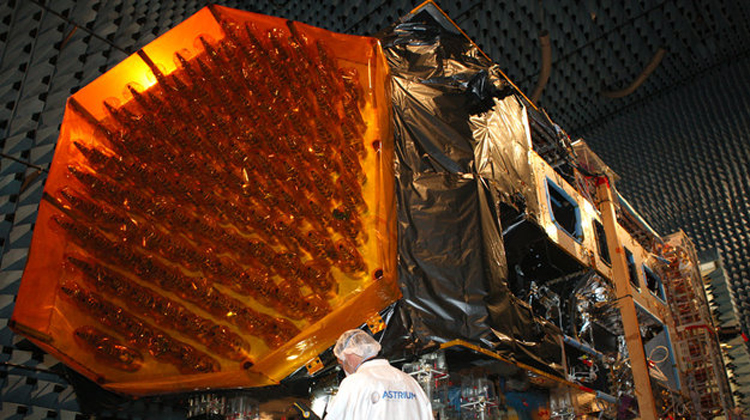
ARTES 8 Alphabus/Alphasat is dedicated to the development and deployment of the Alphasat satellite. Alphasat is being built in partnership between ESA and European operator Inmarsat by Astrium. It is the first satellite to use Alphabus, the new European high-power telecommunications platform jointly developed by Astrium and Thales Alenia Space under a joint contract from ESA and the French space agency, CNES.
Alphabus is the coordinated European response to the increased market demand for larger telecommunication payloads. It is now available on the commercial market to accommodate missions with up to 18 kW of payload power. The new developments within the Alphabus Extension programme will extend the range up to 22 kW.
Alphasat carries a new generation of advanced geomobile communications payload in L-band that will augment Inmarsat’s Broadband Global Area Network (BGAN) service, enabling communications across Europe, Asia, Africa and the Middle East with increased capacity. Weighing more than 6,000kg, Alphasat is planned for launch in 2013 on Ariane 5.
Alphasat also carries four technology demonstration payloads developed through ESA’s Advanced Research in Telecommunications Systems (ARTES) programme.
Laser communication and Ka-band downlink
The advanced laser terminal provides optical communications at 2.8 Gbit/s from Earth observation satellites in low-Earth orbit to a geostationary orbit. A Ka-band transmitter sends the data to a ground station.
Q/V-band communication and propagation
 A repeater explores the use of these frequencies for future applications. In parallel, experiments with the propagation beacon measure the effects of Earth’s atmosphere on radio waves in the band.
A repeater explores the use of these frequencies for future applications. In parallel, experiments with the propagation beacon measure the effects of Earth’s atmosphere on radio waves in the band.
Startracker
A sensor with active pixel detector is included to gain early flight experience on this new product, capable of very accurate and autonomous attitude acquisition. The sensor is highly resistant to the radiation environment in geostationary orbit.
Environmental testing and radiation sensor
The environment effects facility tests electronic components and solid-state materials in the radiation environment of geostationary orbit. A particle spectrometer measures these radiation levels in parallel.
 English
English  Français
Français  العربية
العربية